While looking into Stable Diffusion models for image generation, I came across the Diffusers library from Hugging Face. Diffusers make it extremely easy to load and use models hosted on Hugging Face. It gets rid of the boilerplate code required to run ML models for image, audio, and video generation. It has good documentation and community support built around it. So it was great fun to try it out on google colab. I will go over how you can get started with using the Diffusers library on google colab.
Setup and Installation
If you are new to google colab, it’s easy to log-in on https://colab.research.google.com/ using your google account. It’s free tier is good enough to try out diffusion models.
To start using diffusers, first install diffusers library
pip install diffusers
Loading models using DiffusionPipeline
DiffusionPipeline is the class using which you can load any models hosted on the HuggingFace. The way to load any model from Hugging Face is to provide relative path of the model hosted on their website.
Let’s load runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5 model from HuggingFace.
import torch
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float32)
pipeline.to("cuda")
This will fail with error:
The secret `HF_TOKEN` does not exist in your Colab secrets.
To authenticate with the Hugging Face Hub, create a token in your settings tab (https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens), set it as secret in your Google Colab and restart your session.
You will be able to reuse this secret in all of your notebooks.
You can solve this issue by creating account on huggingface and creating the token here: https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens.
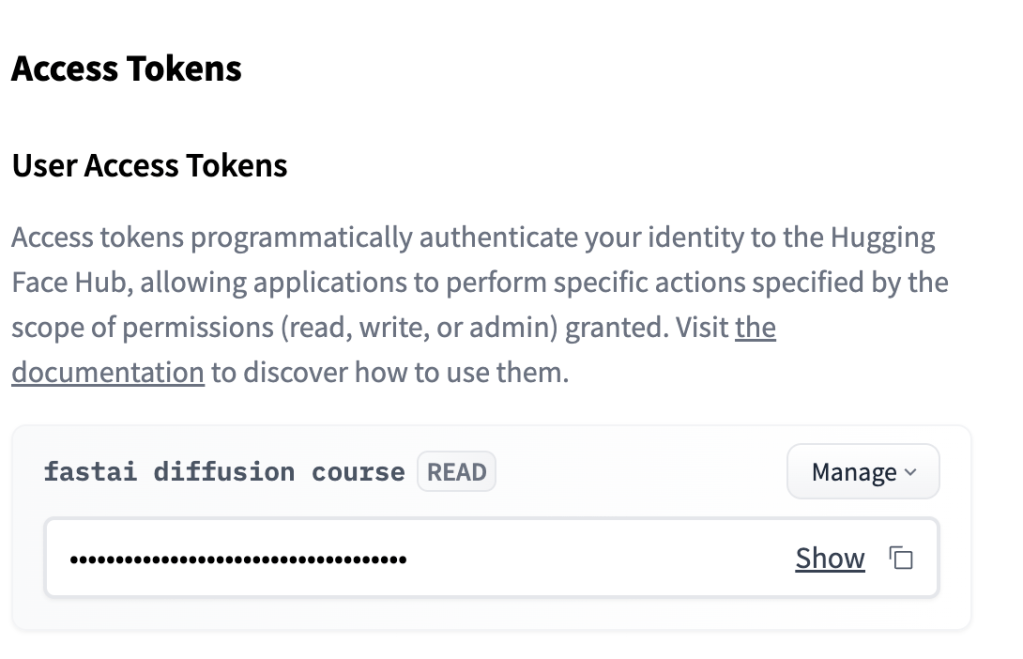
After that, add that token over the secrets section of the notebook as value of HF_TOKEN secret. Pretty straightforward so far 😛

Once access token setup is done, we can load the diffusion pipeline using 4 lines of code mentioned below.
import torch
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained("runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5", torch_dtype=torch.float32)
pipeline.to("cuda")
- runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5 is the model we want to load from Hugging Face
- We are specifying torch.float32 as torch datatype. We will go over why we choose that in next series of blogs.
- By specifying cuda, we are running our model on GPU. google colab free version provides us T4 instance which is good enough to run stable-diffusion-v1-5 version.
Inference
Once the pipeline instance is created as mentioned above, you can generate an image by providing a textual prompt.
image = pipeline("An image of a squirrel", num_inference_steps = 50).images[0]
image

Pretty cool, right? It’s that easy to get started with diffusers. In the next series of blogs, we will try to look at diffusers in depth and identify its pros and cons. Stay tuned.
You can find the above code example on my GitHub along with the Google Colab link.